Wireless Bridge Wireless LAN WLAN Common Term - Shenzhen Haishunbo
802.11a
5 Mbps standard 54Mbps wireless LAN standard 802.11b
11Mbps WLAN Working in the 2.4GHz Band Industry Standard 802.11
Defines quality-of-service (QoS) for wireless LANs, such as VoIP (voice-over IP) support 802.11g
802.11b's successor, providing data rates of up to 54Mbps on the same 2.4GHz band used by 802.11b 802.11h
Supplement to 802.11a to ensure compliance with the European standard 802.11i for 5GHz wireless LAN
Wireless security standard, WPA is a subset of it 802.11j
The 802.11n protocol used in Japan that is equivalent to 802.11h
Expected specification adopted in 2006, this specification will double the transmission rate of 802.11a/g wireless LANs 802.15
Bluetooth-based personal area networks standard 802.16
A set of communication standards for high-capacity metropolitan area networks (MANs), also known as Wireless Man or WiMAX
802.20
Provide 1Mbps wireless metropolitan area network draft within the furthest 15km, plan to work in the licensed frequency band of 3.5GHz 802.1x
Authentication Point Based on Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Access Point
Access point, acting as a hub for wireless users, typically supporting up to 253 concurrent users in a maximum 100m Bluetooth
Bluetooth, short-range (10 to 100m) wireless connection technology as a replacement for connecting mobile phones, handheld PCs, and other personal digital device cables; another alternative is Infrared Circuit Switched Data
Circuit-switched data, based on traditional dial-up data connections for mobile phones, transmission speeds up to 9.6 Kbps
Dynamic Frequency Selection/Dynamic Channel Selection
Dynamic Frequency Selection/Dynamic Channel Selection Allows User Equipment to Select the Clearest Channel in the Radio Frequency Band European Telecommunications Standards Institute
European Telecommunications Standards Institute, Extensible Authentication Protocol for the development of telecom standards in Europe
Extensible authentication protocol to improve the performance of wireless LANs by allowing dynamic addition of authentication modules to wirelessly connected clients and servers. General Packet Radio Service
General Packet Radio Service, a technology that allows always-on cellular networks to provide Internet and corporate network access through mobile phones, with a maximum data rate of 114 Kbps. The average rate in the UK is 42Kbps
Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System (GPS), a system of 24 orbiting satellites orbiting the Earth, which provides position and remote sensing data for ground receivers to indicate geographical position and moving speed. For most devices, positioning accuracy is 10m to 100m range High-Speed ​​Circuit Switched Data
High-speed circuit-switched data, Hiper LAN/1, a protocol that provides faster data transmission (14.4Kbps) over dial-up mobile data connections
802.11b WLAN standard competitor, this technology can provide up to 20Mbps data rate Hiper LAN/2 at 5GHz
Hiper LAN variant, providing up to 54Mbps data rate on the same radio frequency band of HiperLAN/1 Hotspot
Hot spots, which are installed in public places such as airports, train stations, hotels, and cafes to access wireless LANs. With a wireless-enabled laptop or PDA, it provides mobile users high-speed access to the Internet. Infrared Data Association
Infrared Data Standards Association, an enterprise-funded organization responsible for the design and maintenance of international standards compliant with the use of infrared communications links, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
American Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, responsible for the formulation of Quality of Service statements for 802.11x wireless LAN standards
Quality of service, metrics for evaluating transmission quality and error rates, often used as a proxy for network performance, to determine network reliability and serve as a reference for implementing service level related agreements.
Wireless Communications Authority, the UK's Robust Security Network, which standardizes the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands used by wireless LAN devices
RSN, a WPA replacement protocol based on 802.1x and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Transport Layer Security
Transport layer security, Transmit Power Control to ensure uninterrupted data transmission between communications applications and users over wireless LANs and the Internet
Transmission power control allows wireless LAN users to use the minimum transmit power allowed for transmitting data signals when data transmission conflicts with other users. Wired Equivalent Privacy
Wired Equivalent Protocol, the default encryption mechanism used by 802.11x. Including either 40-bit or 128-bit formats, it is considered very insecure. Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance
Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance, the Trade Union Wireless Protected Access that facilitates the compatibility of wireless LAN devices produced by different vendors
Wireless protection access, using rotating keys mechanism to provide more secure protection technology for wireless data transmission, is considered a replacement for WEP WLan
Abbreviation for wireless LAN, also known as Wi-Fi
WI-MAX
Wi-MAX (ie, 802.16) technology has been under development since 2001, and now there are related products on the market. It provides the same data transmission rate as most wired LANs within 30 miles. This technology is Think of it as a way to introduce a large number of broadband connections to remote areas or to cover a wide range of dispersed corporate and campus areas.
The Wi-MAX standard has been split into two variants:
The original Wi-MAX standard of 802.16a, can provide up to 70Mbps data rate for the maximum 30-mile range in the 10GHz and 66GHz bands;
The newly developed Wi-MAX standard of 802.16e can work in the licensed 2GHz to 6GHz band, which makes it possible for mobile devices to use this technology.
The Wi-MAX standard takes into account the deployment of metropolitan area networks and end-user applications, making it an alternative technology for the deployment of next-generation wireless LANs. It allows vendors to standardize on single protocols and core technologies. The latter addresses site-to-site and site-to-user wireless network transmissions.
Pre-provisioning of frequency bands for household equipment and unregistered commercial equipment needs to be re-divided. This technology still has certain problems for some countries in Europe, the Middle East and Asia. However, 802.11a also faces similar problems. The industry hopes that these issues can be solved with the increasing demand of users in neighboring countries.
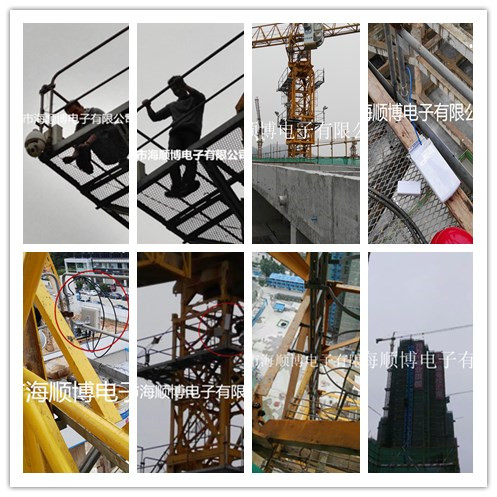
1-50 km Haishunbo Wireless Bridge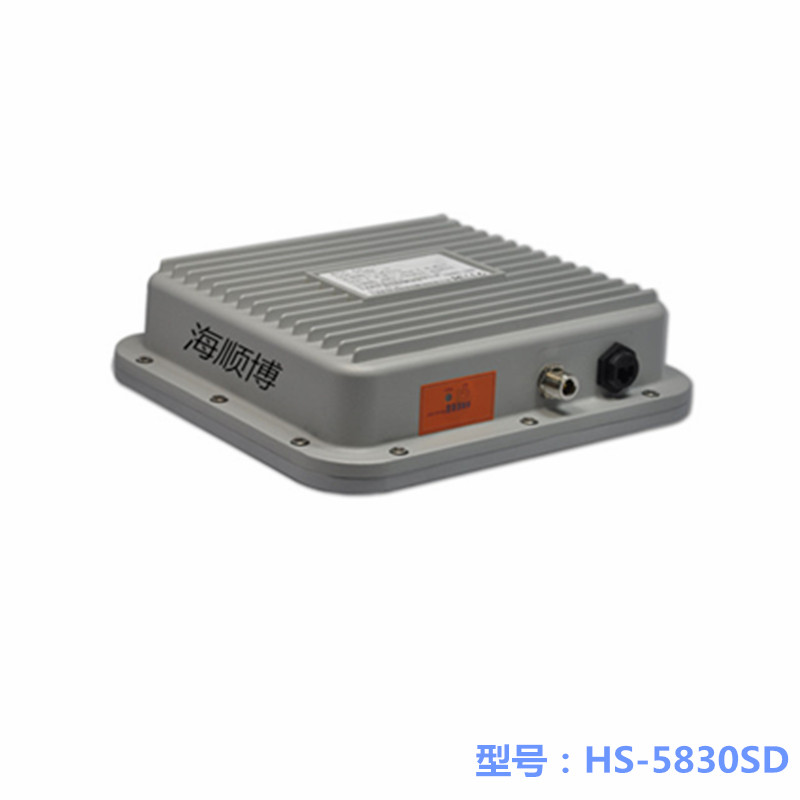
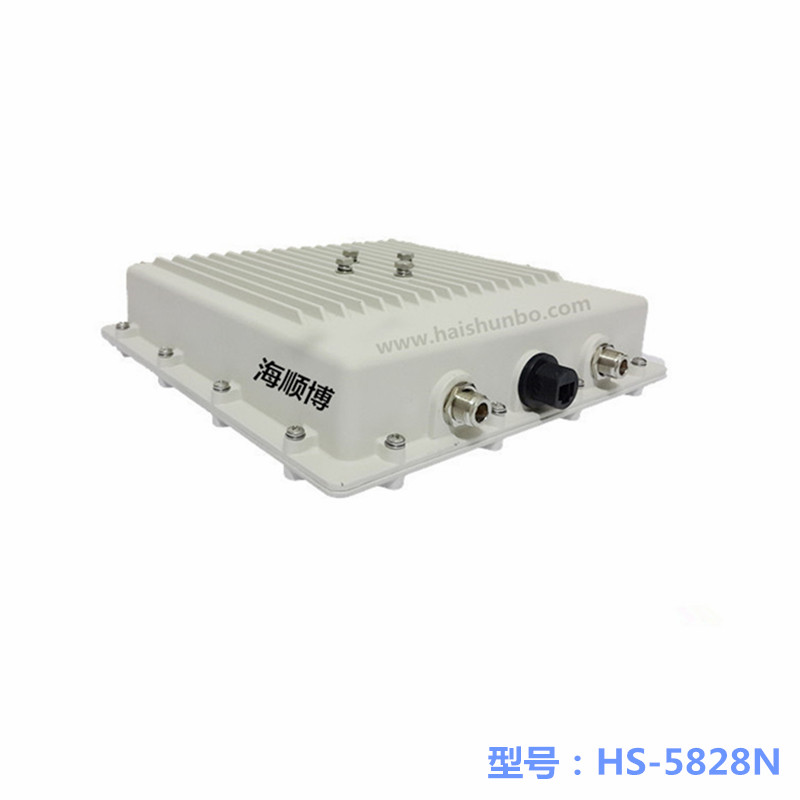
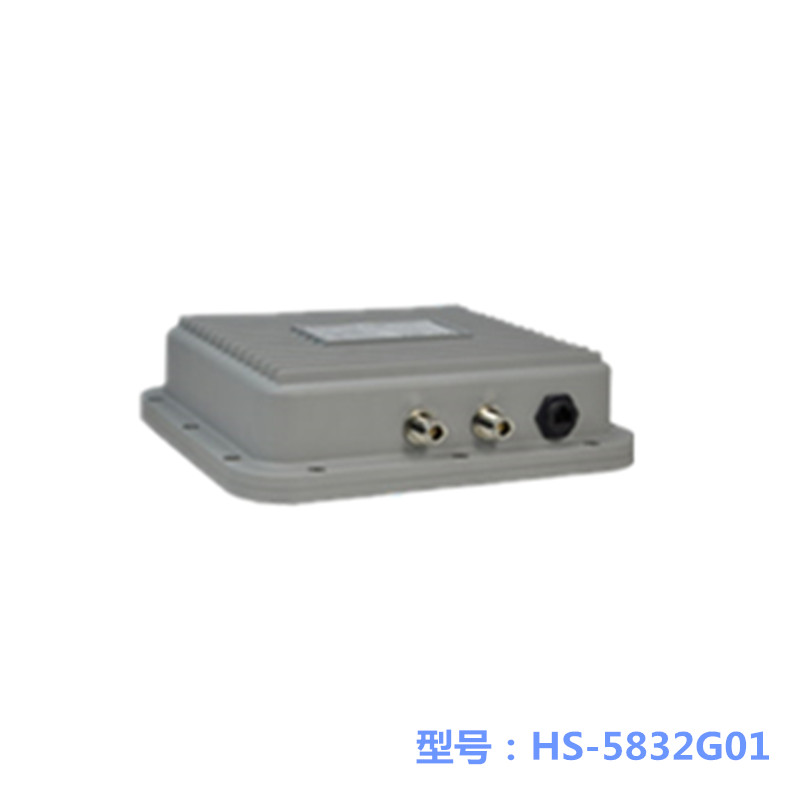
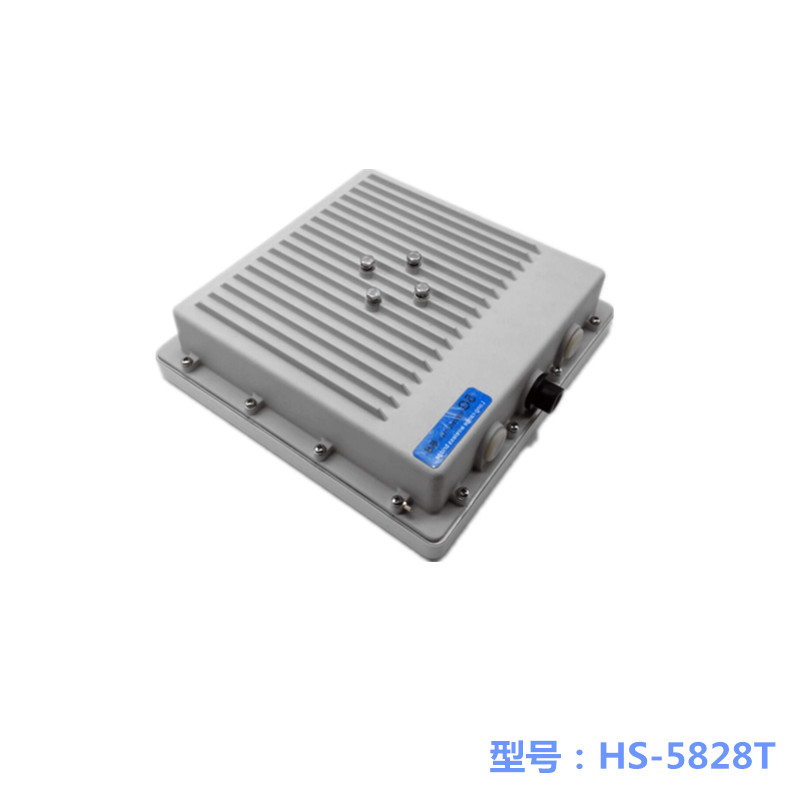



Haishunbo Wireless Bridge Application Case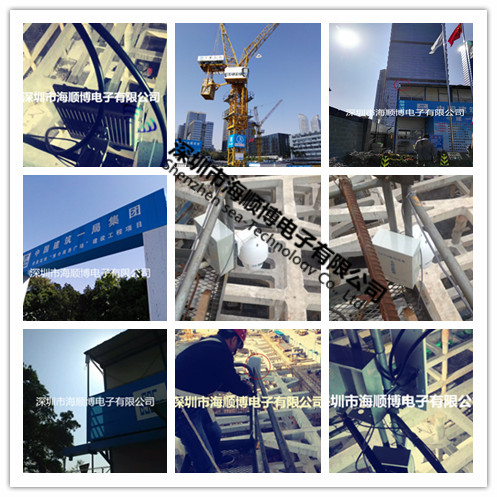





5 Mbps standard 54Mbps wireless LAN standard 802.11b
11Mbps WLAN Working in the 2.4GHz Band Industry Standard 802.11
Defines quality-of-service (QoS) for wireless LANs, such as VoIP (voice-over IP) support 802.11g
802.11b's successor, providing data rates of up to 54Mbps on the same 2.4GHz band used by 802.11b 802.11h
Supplement to 802.11a to ensure compliance with the European standard 802.11i for 5GHz wireless LAN
Wireless security standard, WPA is a subset of it 802.11j
The 802.11n protocol used in Japan that is equivalent to 802.11h
Expected specification adopted in 2006, this specification will double the transmission rate of 802.11a/g wireless LANs 802.15
Bluetooth-based personal area networks standard 802.16
A set of communication standards for high-capacity metropolitan area networks (MANs), also known as Wireless Man or WiMAX
802.20
Provide 1Mbps wireless metropolitan area network draft within the furthest 15km, plan to work in the licensed frequency band of 3.5GHz 802.1x
Authentication Point Based on Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Access Point
Access point, acting as a hub for wireless users, typically supporting up to 253 concurrent users in a maximum 100m Bluetooth
Bluetooth, short-range (10 to 100m) wireless connection technology as a replacement for connecting mobile phones, handheld PCs, and other personal digital device cables; another alternative is Infrared Circuit Switched Data
Circuit-switched data, based on traditional dial-up data connections for mobile phones, transmission speeds up to 9.6 Kbps
Dynamic Frequency Selection/Dynamic Channel Selection
Dynamic Frequency Selection/Dynamic Channel Selection Allows User Equipment to Select the Clearest Channel in the Radio Frequency Band European Telecommunications Standards Institute
European Telecommunications Standards Institute, Extensible Authentication Protocol for the development of telecom standards in Europe
Extensible authentication protocol to improve the performance of wireless LANs by allowing dynamic addition of authentication modules to wirelessly connected clients and servers. General Packet Radio Service
General Packet Radio Service, a technology that allows always-on cellular networks to provide Internet and corporate network access through mobile phones, with a maximum data rate of 114 Kbps. The average rate in the UK is 42Kbps
Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System (GPS), a system of 24 orbiting satellites orbiting the Earth, which provides position and remote sensing data for ground receivers to indicate geographical position and moving speed. For most devices, positioning accuracy is 10m to 100m range High-Speed ​​Circuit Switched Data
High-speed circuit-switched data, Hiper LAN/1, a protocol that provides faster data transmission (14.4Kbps) over dial-up mobile data connections
802.11b WLAN standard competitor, this technology can provide up to 20Mbps data rate Hiper LAN/2 at 5GHz
Hiper LAN variant, providing up to 54Mbps data rate on the same radio frequency band of HiperLAN/1 Hotspot
Hot spots, which are installed in public places such as airports, train stations, hotels, and cafes to access wireless LANs. With a wireless-enabled laptop or PDA, it provides mobile users high-speed access to the Internet. Infrared Data Association
Infrared Data Standards Association, an enterprise-funded organization responsible for the design and maintenance of international standards compliant with the use of infrared communications links, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
American Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, responsible for the formulation of Quality of Service statements for 802.11x wireless LAN standards
Quality of service, metrics for evaluating transmission quality and error rates, often used as a proxy for network performance, to determine network reliability and serve as a reference for implementing service level related agreements.
Wireless Communications Authority, the UK's Robust Security Network, which standardizes the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands used by wireless LAN devices
RSN, a WPA replacement protocol based on 802.1x and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Transport Layer Security
Transport layer security, Transmit Power Control to ensure uninterrupted data transmission between communications applications and users over wireless LANs and the Internet
Transmission power control allows wireless LAN users to use the minimum transmit power allowed for transmitting data signals when data transmission conflicts with other users. Wired Equivalent Privacy
Wired Equivalent Protocol, the default encryption mechanism used by 802.11x. Including either 40-bit or 128-bit formats, it is considered very insecure. Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance
Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance, the Trade Union Wireless Protected Access that facilitates the compatibility of wireless LAN devices produced by different vendors
Wireless protection access, using rotating keys mechanism to provide more secure protection technology for wireless data transmission, is considered a replacement for WEP WLan
Abbreviation for wireless LAN, also known as Wi-Fi
WI-MAX
Wi-MAX (ie, 802.16) technology has been under development since 2001, and now there are related products on the market. It provides the same data transmission rate as most wired LANs within 30 miles. This technology is Think of it as a way to introduce a large number of broadband connections to remote areas or to cover a wide range of dispersed corporate and campus areas.
The Wi-MAX standard has been split into two variants:
The original Wi-MAX standard of 802.16a, can provide up to 70Mbps data rate for the maximum 30-mile range in the 10GHz and 66GHz bands;
The newly developed Wi-MAX standard of 802.16e can work in the licensed 2GHz to 6GHz band, which makes it possible for mobile devices to use this technology.
The Wi-MAX standard takes into account the deployment of metropolitan area networks and end-user applications, making it an alternative technology for the deployment of next-generation wireless LANs. It allows vendors to standardize on single protocols and core technologies. The latter addresses site-to-site and site-to-user wireless network transmissions.
Pre-provisioning of frequency bands for household equipment and unregistered commercial equipment needs to be re-divided. This technology still has certain problems for some countries in Europe, the Middle East and Asia. However, 802.11a also faces similar problems. The industry hopes that these issues can be solved with the increasing demand of users in neighboring countries.
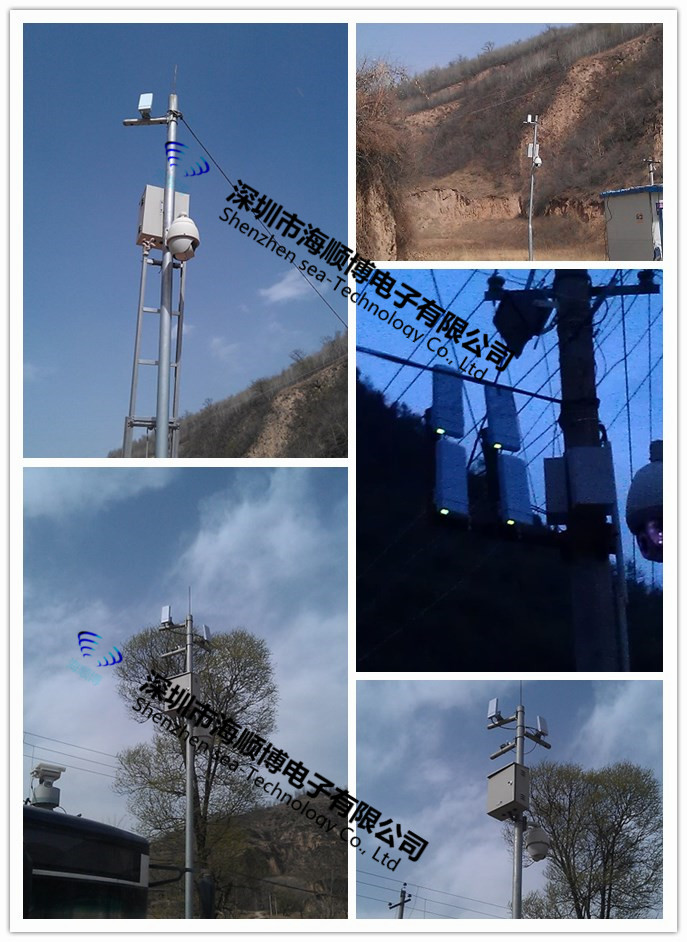
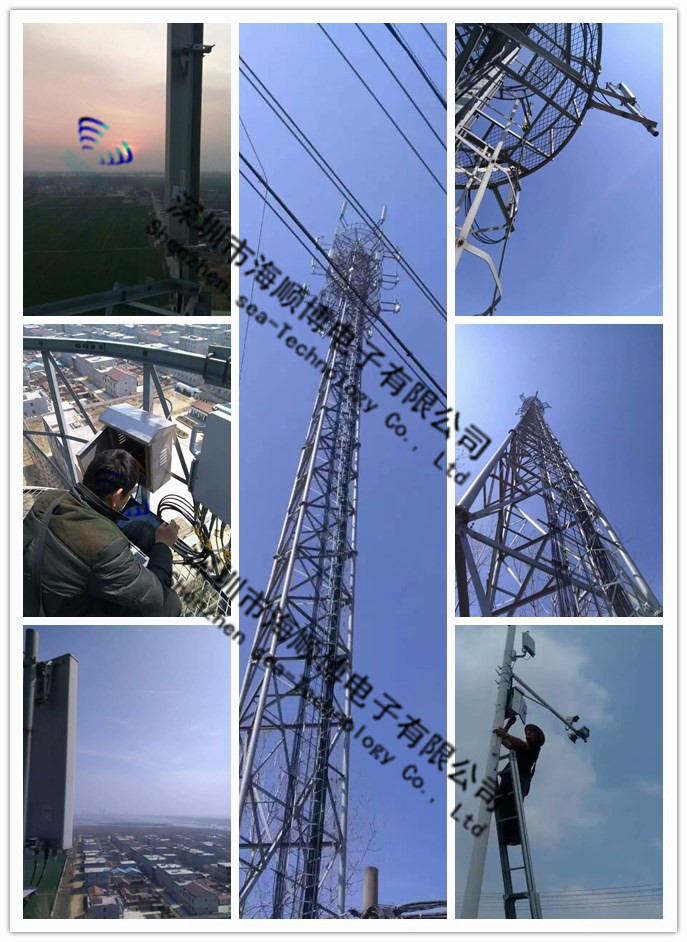
1-50 km Haishunbo Wireless Bridge






Haishunbo Wireless Bridge Application Case






Stainless Steel Casting Parts,Rapid Prototyping Cost,Custom Metal Machining Parts,Complex Machining Part
Guangdong Fenghua Zhuoli Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.fhzlprinter.com